This is an in depth explanation of Lysosomes as a part of the cell. This lecture note is linked to A&P Lecture 1: The Cell
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 1.12
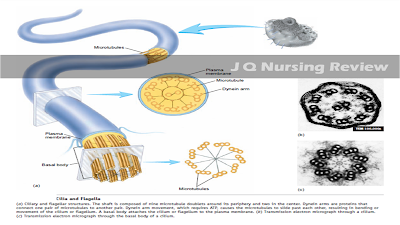
Cilia and Flagella
Cilia are structures that project from the surface of cells and are capable of movement. They vary in number from one to thousands per cell. Cilia are cylindrical in shape, about 10 μm in length and 0.2 μm in diameter, and the shaft of each cilium is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Two centrally located microtubules and nine peripheral pairs of fused microtubules, the so-called 9 2 arrangement, extend from the base to the tip of each cilium. Movement of the microtubules past each other, a process that requires energy from ATP, is responsible for movement of the cilia. Dynein arms, proteins connecting adjacent pairs of microtubules, push the microtubules past each other. A basal body (a modified centriole) is located in the cytoplasm at the base of the cilium. Cilia are numerous on surface cells that line the respiratory tract and the female reproductive tract. In these regions, cilia move in a coordinated fashion, with a power stroke in one direction and a recovery stroke in the opposite direction. Their motion moves materials over the surface of the cells. For example, cilia in the trachea move mucus embedded with dust particles upward and away from the lungs. This action helps keep the lungs clear of debris.
Flagella have a structure similar to cilia but are longer (45 μm). Sperm cells are the only human cells to possess flagella and usually only one flagellum exists per cell. Furthermore, whereas cilia move small particles across the cell surface, flagella move the entire cell. For example, each sperm cell is propelled by a single flagellum. In contrast to cilia, which have a power stroke and a recovery stroke, flagella move in a
wavelike fashion.
Microvilli
Microvilli ) are cylindrically shaped
extensions of the plasma membrane about 0.5–1.0 μm in length and 90 nm in diameter. Normally, many microvilli are on each cell, and they function to increase the cell surface area. A student looking at photographs may confuse microvilli with cilia. Microvilli, however, are only one-tenth to one-twentieth the size of cilia. Individual microvilli can usually be seen only with an electron microscope, whereas cilia can be seen with a light microscope. Microvilli do not move, and they are supported with actin filaments, not microtubules. Microvilli are found in the intestine, kidney, and other areas in which absorption is an important
function. In certain locations of the body, microvilli are highly modified to function as sensory receptors. For example, elongated microvilli in hair cells of the inner ear respond to sound.

No comments:
Post a Comment
We would like to hear from you!
For your inquiries, suggestions and request please don't hesitate to comment or message us with our contact form in our "Contact Us" page above!
Enjoy